I currently own two Zigbee-based dimmer switches from Philipps Hue (the old V1 version). I was always wondering what the different blinking patterns of the LED indicated. Understanding them was not too straightforward. So here is a quick summary: Blinking orange The device is currently in pairing mode, waiting to be paired. A hard-reset andContinue reading “Blinking patterns of Philips Hue Dimmer Switch V1 (RWL021)”
Tag Archives: basics
What is IoT?
IoT is short for Internet of Things. Internet is the worldwide electronic network connecting computers that we all know, but also people and society. And “things” in this case, are products or objects from everyday life, that get “augmented” by adding some form of smartness to them using a microcontroller and network connectivity. IoT devicesContinue reading “What is IoT?”
What is Docker? How does it work?
In short: Docker is a platform and toolkit to develop applications that consist of multiple small containerized components that can be started, updated and replicated independently from each other. How it came to be Factor 1 – Monoliths are hard to handle Humans develop software since the early days of computers. Programming languages have evolvedContinue reading “What is Docker? How does it work?”
720×720 LCD screen using DPI on Raspberry Pi 4
Some weeks ago, I bought a 4inch square LCD screen with 720×720 pixels from Waveshare. However, they did not provide any documentation at all for this specific display, but there was more than enough documentation for all the other displays, e.g. this rectangular one. Thus, I decided to document here how to get this displayContinue reading “720×720 LCD screen using DPI on Raspberry Pi 4”
Subscribe to The Things Network (TTN) using MQTT
The Things Network (TTN) is an open platform for creating a worldwide LoRaWAN network. You can install your own LoRa gateways and register them on TTN so that other TTN users can use your gateways. If you have devices or sensors publishing data over LoRa, you can receive this data using an MQTT broker fromContinue reading “Subscribe to The Things Network (TTN) using MQTT”
Setup a LAMP stack on Ubuntu (e.g. for hosting WordPress)
Mainly as a quick reminder for myself, I write down all the necessary steps to setup a LAMP stack on Ubuntu Linux. LAMP is a combination of software required to serve a dynamic PHP website. L = Linux, A = Apache Webserver, M = MySQL or MariaDB database, P = PHP Step 0: Update packageContinue reading “Setup a LAMP stack on Ubuntu (e.g. for hosting WordPress)”
Node-RED – Install on Linux
Introduction What is Node-RED? Node-RED is an open-source and low-code software, that allows to connect anything with anything. This means, any device that produces data and can be accessed over a network, can be included as a data source or sink in Node-RED. Messages from the devices can be modified or analyzed, processed and thenContinue reading “Node-RED – Install on Linux”
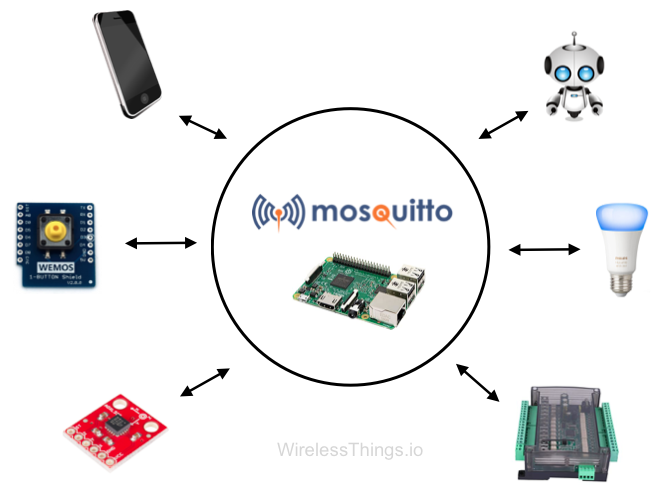
Mosquitto MQTT: Install broker on Linux
In this article, we will discuss how to install an MQTT broker. An MQTT broker (MQTT is short for Message Queue Telemetry Transport) is responsible for delivering messages in a network from publishers to subscribers. The broker receives all messages on different topics from different devices, and filters them according to the subscriptions of otherContinue reading “Mosquitto MQTT: Install broker on Linux”
Grafana – Useful Keyboad Shortcuts
Grafana is easy to use with some shortcuts and key combinations. You can use this list as a reference in the future. You can also download and print a PDF I prepared for you! You can also bring up a shortcut summary in Grafana by clicking Shift + ? in the dashboard. Key / ActionContinue reading “Grafana – Useful Keyboad Shortcuts”
Connect Grafana to InfluxDB and show data
In the previous article about how to set up InfluxDB, we have imported a sample dataset. Now, we want to show this data in Grafana by fetching it from an InfluxDB data source. Step 1: Setup the data source connection Log in to Grafana (usually on http://localhost:3000), and on the left side, click on ConfigurationContinue reading “Connect Grafana to InfluxDB and show data”